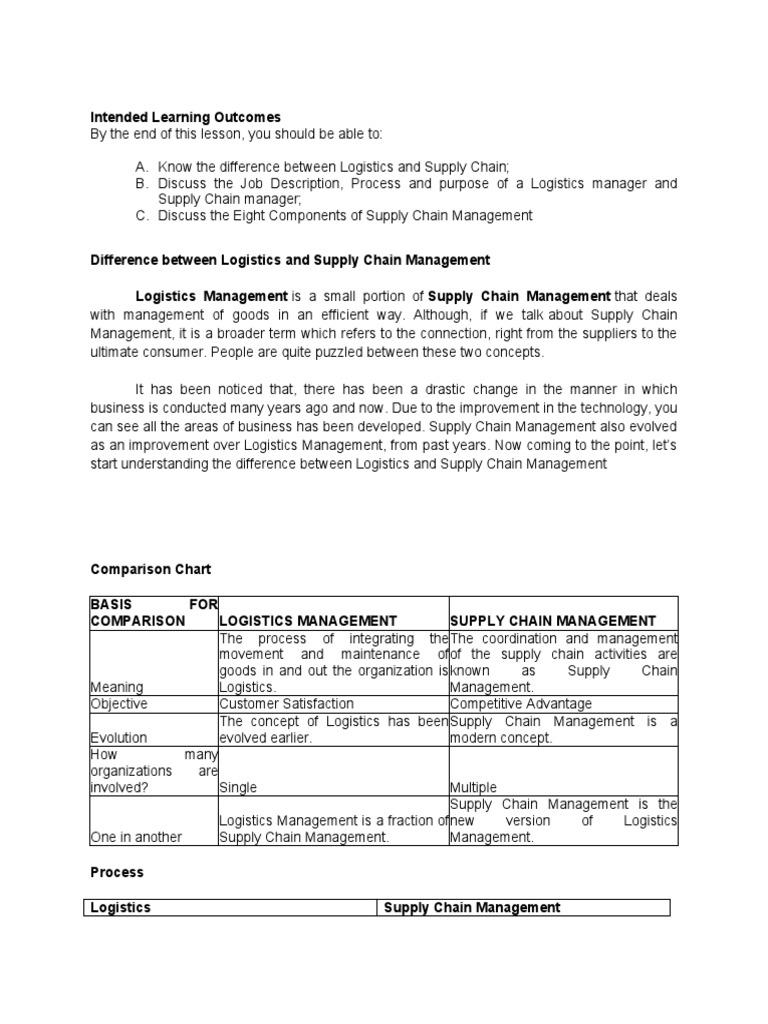
The SCOR Model is a reference process model, developed by Supply Chain Council. This model is widely used across industries. It allows companies to understand their business goals, processes and performance. The software also allows users to compare themselves with their peers and identify areas that need improvement.
The model is divided into three major segments: process modeling, performance measurements and supply chain best practices. The first segment focuses on process modeling. This includes planning, sourcing and making goods. The model also covers market interactions and returns.
This segment also contains more than 150 key indicators (KPIs), that you can use as a way to evaluate the success of your business. For example, if you want to evaluate the quality of products and their cost, then you can determine if your suppliers are providing high-quality products.
You can also review customer returns and analyze the cost savings you could achieve if your suppliers were to reduce their returns rates by 20 percent. You can identify areas in which you could save money by improving processes.

If you're unfamiliar with the SCOR, you may have questions about its operation. The main purpose of the SCOR Model is to help your create an effective and standardized system for management of your supply chain.
It breaks up the supply chain in ideal business processes. Each process is then categorized based on its value to your company. The result is a system that makes it easy to compare and coordinate different supply chain activities within your company and across the entire industry.
The second segment is the performance measurement, which includes metrics you can use to assess the overall success your supply chain operation. These metrics may be used for evaluations in a number of areas, such as inventory control, transportation costs and supplier quality.
Use the data on performance measurement to see how your business is doing in each area and set goals to improve your operation. These measures will only be useful if you actually take action.
The first thing you need to do is make a list of KPIs, which you can track. You can then review these metrics on a monthly basis to determine how well your company is performing in each area.

You should start to consider how your business can implement new processes that will improve your operations and increase your profitability. You can then compare these new processes with those in your existing operations to make sure that they are effective.
This is the perfect way to get your entire team started on improving your company's operations. In addition, the SCOR model provides an opportunity for companies to collaborate with their suppliers and customers by sharing a common language and framework for measuring and analyzing supply chain performance.
FAQ
What are the main products of logistics?
Logistics involves the transportation of goods from point A and point B.
They include all aspects of transport, including packaging, loading, transporting, unloading, storing, warehousing, inventory management, customer service, distribution, returns, and recycling.
Logisticians ensure that the right product reaches the right place at the right time and under safe conditions. Logisticians assist companies in managing their supply chains by providing information such as demand forecasts, stock levels and production schedules.
They also keep track of shipments in transit, monitor quality standards, perform inventories and order replenishment, coordinate with suppliers and vendors, and provide support services for sales and marketing.
What makes a production planner different from a project manger?
The major difference between a Production Planner and a Project Manager is that a Project Manager is often the person responsible for organizing and planning the entire project. While a Production Planner is involved mainly in the planning stage,
Why should you automate your warehouse?
Modern warehousing is becoming more automated. Increased demand for efficient and faster delivery has resulted in a rise in e-commerce.
Warehouses need to adapt quickly to meet changing needs. To do so, they must invest heavily in technology. Automating warehouses is a great way to save money. Here are some of the reasons automation is worth your investment:
-
Increases throughput/productivity
-
Reduces errors
-
Accuracy is improved
-
Safety is boosted
-
Eliminates bottlenecks
-
This allows companies to scale easily
-
It makes workers more efficient
-
The warehouse can be viewed from all angles.
-
Enhances customer experience
-
Improves employee satisfaction
-
It reduces downtime, and increases uptime
-
This ensures that quality products are delivered promptly
-
Removing human error
-
Helps ensure compliance with regulations
What can I do to learn more about manufacturing?
Practical experience is the best way of learning about manufacturing. You can read books, or watch instructional videos if you don't have the opportunity to do so.
Statistics
- In the United States, for example, manufacturing makes up 15% of the economic output. (twi-global.com)
- Job #1 is delivering the ordered product according to specifications: color, size, brand, and quantity. (netsuite.com)
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
- According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), China is the top manufacturer worldwide by 2019 output, producing 28.7% of the total global manufacturing output, followed by the United States, Japan, Germany, and India.[52][53] (en.wikipedia.org)
External Links
How To
How to Use the Just-In-Time Method in Production
Just-in-time is a way to cut costs and increase efficiency in business processes. It allows you to get the right amount resources at the right time. This means that your only pay for the resources you actually use. The term was first coined by Frederick Taylor, who developed his theory while working as a foreman in the early 1900s. After observing how workers were paid overtime for late work, he realized that overtime was a common practice. He then concluded that if he could ensure that workers had enough time to do their job before starting to work, this would improve productivity.
JIT teaches you to plan ahead and prepare everything so you don’t waste time. It is important to look at your entire project from beginning to end and ensure that you have enough resources to handle any issues that may arise. You can anticipate problems and have enough equipment and people available to fix them. This will prevent you from spending extra money on unnecessary things.
There are different types of JIT methods:
-
Demand-driven: This JIT is where you place regular orders for the parts/materials that are needed for your project. This will allow for you to track the material that you have left after using it. This will let you know how long it will be to produce more.
-
Inventory-based : You can stock the materials you need in advance. This allows you to forecast how much you will sell.
-
Project-driven: This method allows you to set aside enough funds for your project. If you know the amount you require, you can buy the materials you need.
-
Resource-based JIT : This is probably the most popular type of JIT. You assign certain resources based off demand. You might assign more people to help with orders if there are many. If there aren't many orders, you will assign fewer people.
-
Cost-based: This is a similar approach to resource-based but you are not only concerned with how many people you have, but also how much each one costs.
-
Price-based: This is similar to cost-based but instead of looking at individual workers' salaries, you look at the total company price.
-
Material-based: This is quite similar to cost-based, but instead of looking at the total cost of the company, you're concerned with how much raw materials you spend on average.
-
Time-based: This is another variation of resource-based JIT. Instead of focusing solely on the amount each employee costs, focus on how long it takes for the project to be completed.
-
Quality-based: This is yet another variation of resource-based JIT. Instead of focusing on the cost of each worker or how long it takes, think about how high quality your product is.
-
Value-based JIT: This is the latest form of JIT. In this scenario, you're not concerned about how products perform or whether customers expect them to meet their expectations. Instead, you are focused on adding value to the marketplace.
-
Stock-based is an inventory-based system that measures the number of items produced at any given moment. It is used when production goals are met while inventory is kept to a minimum.
-
Just-in-time planning (JIT): This is a combination JIT and supply-chain management. It's the process of scheduling delivery of components immediately after they are ordered. It's important because it reduces lead times and increases throughput.