
Whether it is for a new project or a routine work, Industrial Engineering Managers are a critical member of the team. They play a crucial role in guiding staff members and improving production output. They coordinate the design and layout of the factory floor, as well as overseeing the implementation and maintenance of procedures and processes. Additionally, they offer technical knowledge and expertise that can be used to aid in the development of new products or processes.
They are responsible in developing and maintaining effective manufacturing processes. This requires the knowledge of the latest trends in automation and robotics. They need to ensure safety and health compliance, as well as monitor and maintain industrial operations. They also supervise the use of raw materials and consumables. They also carry out studies to improve workflow efficiency and space use. The manager supervises all work projects including product cost reduction, cycle time and process improvement. They also manage preventative maintenance schedules.
In collaboration with other teams, the manager develops new processes, streamlines operations, and improves efficiency. He or she is also responsible for the design and installation, as well as renovations to facilities. Managers are responsible for communicating technical information with non-technical stakeholder as part of their project management. Managers also ensure that resources are available for their teams. They also visit suppliers' facilities. He or she advocates for team members and ensures quality compliance guidelines.

Industrial engineers managers are expected to be creative and highly motivated. They must be able walk and climb for 8 to 12 hours each day and can work in extreme heat and cold. In addition, they should be able interact with all levels.
An engineering degree or related field is required for Industrial Engineering Managers. They must also possess at least five year's experience in the industry. Some employers prefer candidates with a postgraduate degree. Some employers prefer candidates with postgraduate education.
Industrial Engineering Managers are responsible for the development and creation of new products. They are skilled in problem solving and quality improvement. They thrive in a collaborative atmosphere. The manager is most successful when he or she is able to facilitate employees' growth.
Industrial Engineers excel at streamlining operations, and cutting down costs. They are well-versed in manufacturing processes and love meeting deadlines. They have also worked in human resources, logistics and vendor/supplier relations. They can set goals, manage procedures, and create budgets. They can also plan strategies to improve efficiency of engineering projects.
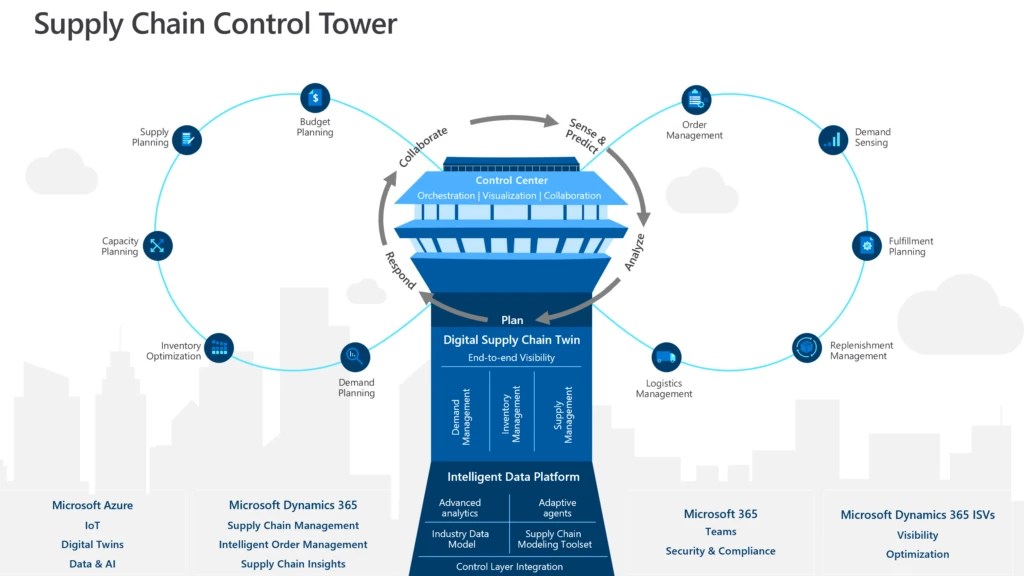
The industrial engineering manager may be responsible for the design and execution of new manufacturing procedures or operating equipment. They are responsible for developing plans to implement new equipment or operating methods according to established standards and guidelines. They are responsible for overseeing the implementation of waste elimination plans. They are also responsible to assess the labor productivity in the factory.
Industrial engineering managers can contribute their expertise to the development of strategies for increasing productivity, creating new products and managing human resource. They can also assist in improving the efficiency of existing processes.
FAQ
Can certain manufacturing steps be automated?
Yes! Yes. The Egyptians invented the wheel thousands of years ago. To help us build assembly lines, we now have robots.
Robotics is used in many manufacturing processes today. These include:
-
Robots for assembly line
-
Robot welding
-
Robot painting
-
Robotics inspection
-
Robots that create products
Automation can be applied to manufacturing in many other ways. 3D printing makes it possible to produce custom products in a matter of days or weeks.
Why automate your factory?
Modern warehouses have become more dependent on automation. E-commerce has brought increased demand for more efficient and quicker delivery times.
Warehouses must adapt quickly to meet changing customer needs. In order to do this, they need to invest in technology. Automation of warehouses offers many benefits. Here are some of the reasons automation is worth your investment:
-
Increases throughput/productivity
-
Reduces errors
-
Increases accuracy
-
Boosts safety
-
Eliminates bottlenecks
-
This allows companies to scale easily
-
This makes workers more productive
-
Gives you visibility into all that is happening in your warehouse
-
Enhances customer experience
-
Improves employee satisfaction
-
This reduces downtime while increasing uptime
-
You can be sure that high-quality products will arrive on time
-
Removing human error
-
It helps ensure compliance with regulations
What types of jobs can you find in logistics
Logistics can offer many different jobs. Some examples are:
-
Warehouse workers: They load and unload trucks, pallets, and other cargo.
-
Transport drivers - These are people who drive trucks and trailers to transport goods or perform pick-ups.
-
Freight handlers: They sort and package freight in warehouses.
-
Inventory managers: They are responsible for the inventory and management of warehouses.
-
Sales representatives - They sell products to customers.
-
Logistics coordinators - They plan and organize logistics operations.
-
Purchasing agents are those who purchase goods and services for the company.
-
Customer service representatives – They answer emails and phone calls from customers.
-
Shipping clerks – They process shipping orders, and issue bills.
-
Order fillers are people who fill orders based only on what was ordered.
-
Quality control inspectors (QCI) - They inspect all incoming and departing products for potential defects.
-
Others - There are many other types of jobs available in logistics, such as transportation supervisors, cargo specialists, etc.
What do you mean by warehouse?
Warehouses and storage facilities are where goods are kept before being sold. It can be an indoor space or an outdoor area. Sometimes, it can be both an indoor and outdoor space.
What are the goods of logistics?
Logistics are the activities involved in moving goods from point A to point B.
They include all aspects of transport, including packaging, loading, transporting, unloading, storing, warehousing, inventory management, customer service, distribution, returns, and recycling.
Logisticians ensure the product reaches its destination in the most efficient manner. They help companies manage their supply chain efficiency by providing information on demand forecasts, stock levels, production schedules, and availability of raw materials.
They also keep track of shipments in transit, monitor quality standards, perform inventories and order replenishment, coordinate with suppliers and vendors, and provide support services for sales and marketing.
Statistics
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
- You can multiply the result by 100 to get the total percent of monthly overhead. (investopedia.com)
- Job #1 is delivering the ordered product according to specifications: color, size, brand, and quantity. (netsuite.com)
- [54][55] These are the top 50 countries by the total value of manufacturing output in US dollars for its noted year according to World Bank.[56] (en.wikipedia.org)
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
External Links
How To
How to use Lean Manufacturing in the production of goods
Lean manufacturing is an approach to management that aims for efficiency and waste reduction. It was created in Japan by Taiichi Ohno during the 1970s and 80s. He received the Toyota Production System award (TPS), from Kanji Toyoda, founder of TPS. Michael L. Watkins published the original book on lean manufacturing, "The Machine That Changed the World," in 1990.
Lean manufacturing can be described as a set or principles that are used to improve quality, speed and cost of products or services. It emphasizes the elimination and minimization of waste in the value stream. Lean manufacturing is also known as just in time (JIT), zero defect total productive maintenance(TPM), and five-star (S). Lean manufacturing eliminates non-value-added tasks like inspection, rework, waiting.
Lean manufacturing can help companies improve their product quality and reduce costs. Additionally, it helps them achieve their goals more quickly and reduces employee turnover. Lean Manufacturing is one of the most efficient ways to manage the entire value chains, including suppliers and customers as well distributors and retailers. Lean manufacturing is widely used in many industries. Toyota's philosophy has been a key driver of success in many industries, including automobiles and electronics.
Five fundamental principles underlie lean manufacturing.
-
Define Value - Identify the value your business adds to society and what makes you different from competitors.
-
Reduce Waste – Eliminate all activities that don't add value throughout the supply chain.
-
Create Flow: Ensure that the work process flows without interruptions.
-
Standardize and Simplify – Make processes as consistent, repeatable, and as simple as possible.
-
Build Relationships- Develop personal relationships with both internal as well as external stakeholders.
Although lean manufacturing has always been around, it is gaining popularity in recent years because of a renewed interest for the economy after 2008's global financial crisis. Many companies have adopted lean manufacturing methods to increase their marketability. In fact, some economists believe that lean manufacturing will be an important factor in economic recovery.
Lean manufacturing has many benefits in the automotive sector. These include improved customer satisfaction, reduced inventory levels, lower operating costs, increased productivity, and better overall safety.
It can be applied to any aspect of an organisation. Lean manufacturing is most useful in the production sector of an organisation because it ensures that each step in the value-chain is efficient and productive.
There are three types principally of lean manufacturing:
-
Just-in Time Manufacturing: This lean manufacturing method is commonly called "pull systems." JIT is a process in which components can be assembled at the point they are needed, instead of being made ahead of time. This approach reduces lead time, increases availability and reduces inventory.
-
Zero Defects Manufacturing, (ZDM): ZDM is focused on ensuring that no defective products leave the manufacturing facility. If a part is required to be repaired on the assembly line, it should not be scrapped. This is true even for finished products that only require minor repairs prior to shipping.
-
Continuous Improvement (CI: Continuous improvement aims to increase the efficiency of operations by constantly identifying and making improvements to reduce or eliminate waste. Continuous Improvement (CI) involves continuous improvement in processes, people, tools, and infrastructure.