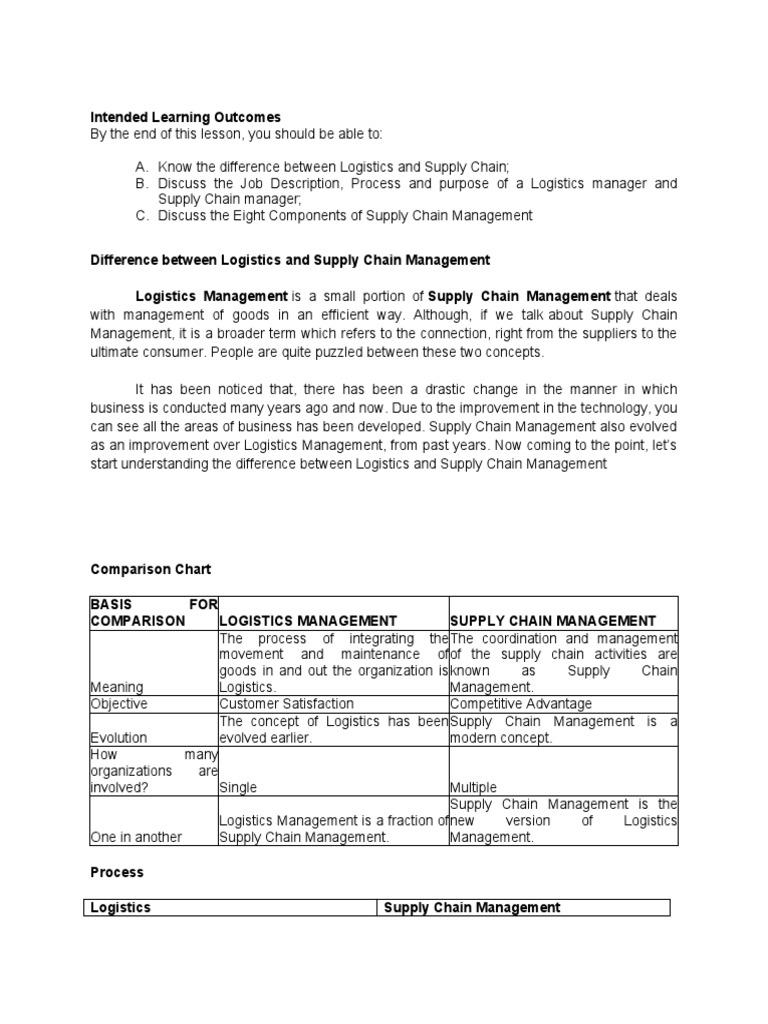
The United States is suffering a decline in manufacturing jobs. This has affected the noncollege educated workforce. This includes Black workers and minorities. These groups have been left behind by the decline in manufacturing jobs. Here's a look into how many people are being left behind.
Trends in Manufacturing Employment
A major question about trends in US manufacturing employment in 2019 is the impact of globalization. The industry employs approximately 40 million people but is losing 3.5 million jobs each year. This decline in employment is due to macroeconomic factors such as taxation, government spending, and Federal Reserve actions.
There is increased competition in the manufacturing sector for entry-level workers. Since the peak in the early years of the twentieth century, the percentage of manufacturing jobs has fallen steadily. Manufacturing accounted for nearly 32 percent of the workforce in 1952. By 2019, that figure has dropped to eight percent. A few economists don't consider this to be a manufacturing slump. However, it is lower than the average during a recession. For example, the ISM Index is 47.2 which is higher than the low 40s in a recession.
The eight census regions had wildly different levels of manufacturing employment in the United States. Northeast had the highest concentration of manufacturing jobs. In comparison, the lowest concentration of manufacturing employment was in the mid-Atlantic states.
Trends in manufacturing output
The US manufacturing sector is one of the most important indicators for the economy. The economic recovery that occurred in the third quarter of 2016 is a sign of sustained growth. Manufacturers still have many challenges. In addition to rising costs, it is getting harder to find raw materials and components, as well as labor. Abhijit Bourde examines five major trends that affect the US's manufacturing sector. He also discusses the impact of these changes on small- and mid-sized companies.
Older individuals are less likely, however, to believe that US manufacturing output has declined. About half of those aged 50-64 believe that manufacturing output has increased over the past three years, while 39% of those between 18 and 29 are more optimistic. Also, income levels seem to affect perceptions about manufacturing output. People earning $100,000 or more per year are more likely to say manufacturing output is higher, while those earning $30,000-49999 are more likely to say manufacturing output has decreased.
FAQ
What is the difference in Production Planning and Scheduling, you ask?
Production Planning (PP), is the process of deciding what production needs to take place at any given time. This is accomplished by forecasting the demand and identifying production resources.
Scheduling involves the assignment of dates and times to tasks in order to complete them within the timeframe.
What does manufacturing mean?
Manufacturing Industries is a group of businesses that produce goods for sale. These products are sold to consumers. These companies use a variety processes such as distribution, retailing and management to accomplish their purpose. They manufacture goods from raw materials using machines and other equipment. This includes all types of manufactured goods, including food items, clothing, building supplies, furniture, toys, electronics, tools, machinery, vehicles, pharmaceuticals, medical devices, chemicals, and many others.
What is the role and responsibility of a Production Planner?
Production planners ensure all aspects of the project are delivered within time and budget. A production planner ensures that the service and product meet the client's expectations.
Why is logistics important in manufacturing?
Logistics are an essential part of any business. They are essential to any business's success.
Logistics plays a significant role in reducing cost and increasing efficiency.
What are the essential elements of running a logistics firm?
To be a successful businessman in logistics, you will need many skills and knowledge. For clients and suppliers to be successful, you need to have excellent communication skills. You should be able analyse data and draw inferences. You must be able to work well under pressure and handle stressful situations. You need to be innovative and creative to come up with new ways to increase efficiency. To motivate and guide your team towards reaching organizational goals, you must have strong leadership skills.
To meet tight deadlines, you must also be efficient and organized.
Statistics
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
- According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), China is the top manufacturer worldwide by 2019 output, producing 28.7% of the total global manufacturing output, followed by the United States, Japan, Germany, and India.[52][53] (en.wikipedia.org)
- Job #1 is delivering the ordered product according to specifications: color, size, brand, and quantity. (netsuite.com)
- You can multiply the result by 100 to get the total percent of monthly overhead. (investopedia.com)
External Links
How To
How to use the Just In-Time Production Method
Just-in-time is a way to cut costs and increase efficiency in business processes. It is a process where you get the right amount of resources at the right moment when they are needed. This means that only what you use is charged to your account. Frederick Taylor first coined this term while working in the early 1900s as a foreman. Taylor observed that overtime was paid to workers if they were late in working. He then concluded that if he could ensure that workers had enough time to do their job before starting to work, this would improve productivity.
JIT is a way to plan ahead and make sure you don't waste any money. Also, you should look at the whole project from start-to-finish and make sure you have the resources necessary to address any issues. You will have the resources and people to solve any problems you anticipate. This will ensure that you don't spend more money on things that aren't necessary.
There are different types of JIT methods:
-
Demand-driven JIT: This is a JIT that allows you to regularly order the parts/materials necessary for your project. This will allow to track how much material has been used up. It will also allow you to predict how long it takes to produce more.
-
Inventory-based: You stock materials in advance to make your projects easier. This allows you to predict how much you can expect to sell.
-
Project-driven: This is an approach where you set aside enough funds to cover the cost of your project. Knowing how much money you have available will help you purchase the correct amount of materials.
-
Resource-based JIT: This is the most popular form of JIT. This is where you assign resources based upon demand. You might assign more people to help with orders if there are many. If you don’t have many orders you will assign less people to the work.
-
Cost-based : This is similar in concept to resource-based. But here, you aren't concerned about how many people your company has but how much each individual costs.
-
Price-based: This is a variant of cost-based. However, instead of focusing on the individual workers' costs, this looks at the total price of the company.
-
Material-based - This is a variant of cost-based. But instead of looking at the total company cost, you focus on how much raw material you spend per year.
-
Time-based JIT: This is another variant of resource-based JIT. Instead of focusing on how much each employee costs, you focus on how long it takes to complete the project.
-
Quality-based JIT is another variant of resource-based JIT. Instead of looking at the labor costs and time it takes to make a product, think about its quality.
-
Value-based JIT: This is the latest form of JIT. This is where you don't care about how the products perform or whether they meet customers' expectations. Instead, your focus is on the value you bring to the market.
-
Stock-based: This is an inventory-based method that focuses on the actual number of items being produced at any given time. It's useful when you want maximum production and minimal inventory.
-
Just-in time (JIT), planning: This is a combination JIT/supply chain management. It refers to the process of scheduling the delivery of components as soon as they are ordered. This is important as it reduces lead time and increases throughput.