
In classical economics, there are three basic sectors. These three basic sectors can be divided into manufacturing, financial activities, and services. Businesses are classified based on their characteristics and risk. Each of these three sectors is described below. Below is a summary of the businesses that each sector has. If you are interested, you can explore the information further. These categories do not have to be mutually exclusive.
Economic activity
Factors that are used to produce, inputs, or outputs affect the country's economic activity. The demand for particular goods or services is often the determinant of a region’s economic activity. There are two types: primary and secondary economic activity. Primary economic activities produce goods and services that satisfy human needs. While secondary economic activities add value by combining raw materials into a better product, they are not as valuable. Manufacturing and processing are two examples of secondary activities.
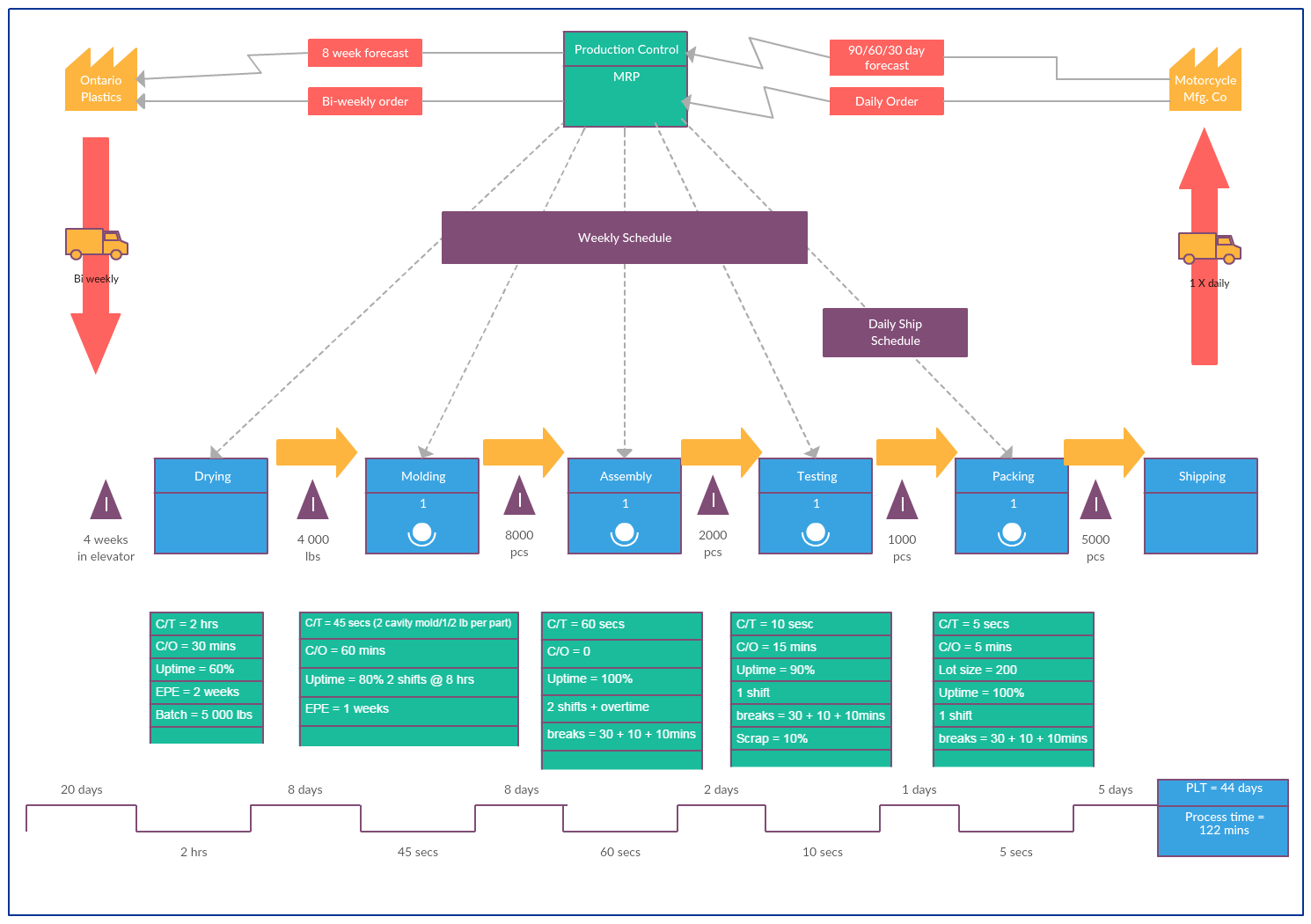
Classification of Businesses
Business classification is the process of dividing businesses into groups based on the type of activities they perform. There are two main types of business classification: primary and secundary. Primary businesses are those that use natural resources to extract them and then exchange them. The second type of business processes and transforms raw materials into products that are ready for consumption. There are numerous differences between these two types of businesses. These are just a few of the differences between the two types. The information in this article will help you to decide which type is right for your business.
Characteristics
The following discussion explains the differences between the primary, secondary, and tertiary sectors and focuses on how each type of sector affects the economy. First, let's define sectors. Sectors are unique economic entities, and they respond differently to various factors. These situations may arise from repeated events such as business cycles or single events such as technological advances. These characteristics can help identify the most viable sector and determine their relative importance to an economy.
Risques
Industry risk is the variation of performance across industries and among companies. This can be assessed by looking at the variance in profitability and return on equity (ROE). This can be adjusted depending on industry to reflect the performance stock markets. A company that makes steel is high-risk because of the possibility for major earthquakes in the area. A study of such risks may help investors determine which sectors are more volatile.
Investments
While some investors may invest in specific companies or sectors, others might choose to invest in broader areas. Sectors can be found both in mutual funds as well as exchange-traded funds. They are safer and have lower risks. Additionally, sector investing has become a very popular investment strategy. This article will help you identify the best investments. Continue reading to find out more. Check out our free resource area for more information.
FAQ
What are the 4 types manufacturing?
Manufacturing refers the process of turning raw materials into useful products with machines and processes. It includes many different activities like designing, building and testing, packaging, shipping and selling, as well as servicing.
How can manufacturing avoid production bottlenecks
To avoid production bottlenecks, ensure that all processes run smoothly from the moment you receive your order to the time the product ships.
This includes both quality control and capacity planning.
This can be done by using continuous improvement techniques, such as Six Sigma.
Six Sigma is a management method that helps to improve quality and reduce waste.
It seeks to eliminate variation and create consistency in your work.
What are the goods of logistics?
Logistics involves the transportation of goods from point A and point B.
They cover all aspects of transportation, such as packing, loading, transporting and unloading.
Logisticians ensure that the right product reaches the right place at the right time and under safe conditions. Logisticians help companies improve their supply chain efficiency by providing information about demand forecasts and stock levels, production schedules, as well as availability of raw materials.
They coordinate with vendors and suppliers, keep track of shipments, monitor quality standards and perform inventory and order replenishment.
Statistics
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
- According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), China is the top manufacturer worldwide by 2019 output, producing 28.7% of the total global manufacturing output, followed by the United States, Japan, Germany, and India.[52][53] (en.wikipedia.org)
- You can multiply the result by 100 to get the total percent of monthly overhead. (investopedia.com)
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
External Links
How To
How to use Lean Manufacturing in the production of goods
Lean manufacturing is a management system that aims at increasing efficiency and reducing waste. It was first developed in Japan in the 1970s/80s by Taiichi Ahno, who was awarded the Toyota Production System (TPS), award from KanjiToyoda, the founder of TPS. Michael L. Watkins published the original book on lean manufacturing, "The Machine That Changed the World," in 1990.
Lean manufacturing is often described as a set if principles that help improve the quality and speed of products and services. It is about eliminating defects and waste from all stages of the value stream. Lean manufacturing can be described as just-in–time (JIT), total productive maintenance, zero defect (TPM), or even 5S. Lean manufacturing focuses on eliminating non-value-added activities such as rework, inspection, and waiting.
Lean manufacturing not only improves product quality but also reduces costs. Companies can also achieve their goals faster by reducing employee turnover. Lean manufacturing is considered one of the most effective ways to manage the entire value chain, including suppliers, customers, distributors, retailers, and employees. Lean manufacturing is widely practiced in many industries around the world. Toyota's philosophy has been a key driver of success in many industries, including automobiles and electronics.
Lean manufacturing is based on five principles:
-
Define Value - Identify the value your business adds to society and what makes you different from competitors.
-
Reduce Waste – Eliminate all activities that don't add value throughout the supply chain.
-
Create Flow. Ensure that your work is uninterrupted and flows seamlessly.
-
Standardize and simplify – Make processes as repeatable and consistent as possible.
-
Build relationships - Develop and maintain personal relationships with both your internal and external stakeholders.
Lean manufacturing isn’t new, but it has seen a renewed interest since 2008 due to the global financial crisis. To increase their competitiveness, many businesses have turned to lean manufacturing. According to some economists, lean manufacturing could be a significant factor in the economic recovery.
Lean manufacturing is now becoming a common practice in the automotive industry, with many benefits. These include higher customer satisfaction levels, reduced inventory levels as well as lower operating costs.
It can be applied to any aspect of an organisation. This is because it ensures efficiency and effectiveness in all stages of the value chain.
There are three main types of lean manufacturing:
-
Just-in-Time Manufacturing (JIT): This type of lean manufacturing is commonly referred to as "pull systems." JIT stands for a system where components are assembled on the spot rather than being made in advance. This approach reduces lead time, increases availability and reduces inventory.
-
Zero Defects Manufacturing, (ZDM): ZDM is focused on ensuring that no defective products leave the manufacturing facility. It is better to repair a part than have it removed from the production line if it needs to be fixed. This also applies to finished products that need minor repairs before being shipped.
-
Continuous Improvement (CI: Continuous improvement aims to increase the efficiency of operations by constantly identifying and making improvements to reduce or eliminate waste. Continuous improvement refers to continuous improvement of processes as well people and tools.